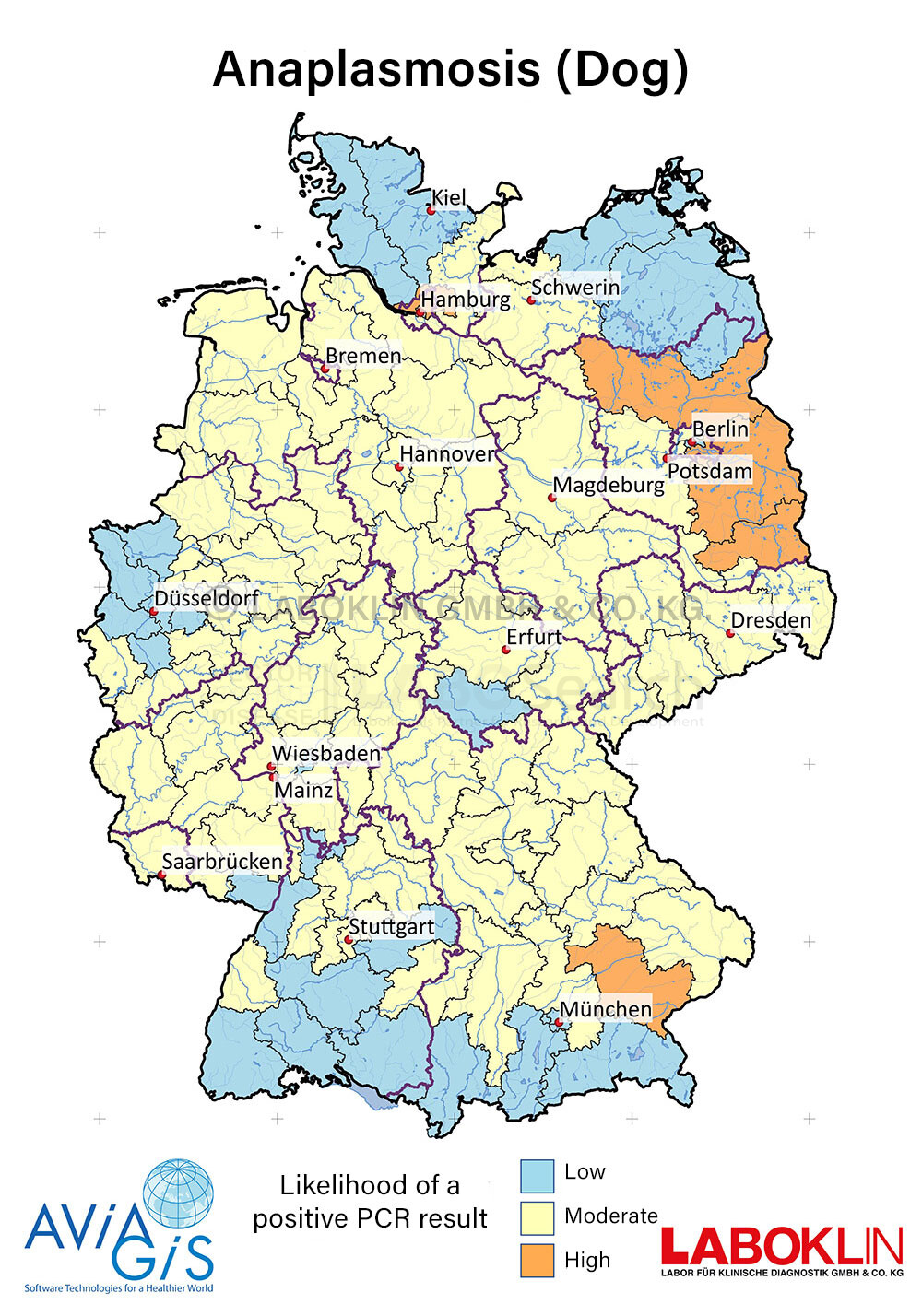
- Granulocytic anaplasmosis in dogs, cats, horses, wildlife and others
- Zoonotic potential: human granulocytic anaplasmosis
- Vector: Ixodes persulcatus complex (in Germany mainly Ixodes ricinus)
- Blood transfusion as another risk of transmission
- Direct detection methods
- PCR (positive result indicative for acute infection)
- Detection of morulae in the blood smear (less sensitive compared to PCR)
- Indirect detection methods (positive result indicative for pathogen contact in the past, paired serum samples necessary for detection of potential infection)
- Antibody-ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)
- IFAT (immunofluorescence antibody test)
- Fever as the most prominent clinical sign
- Thrombocytopenia as the most prominent hematological finding
Amounts of positive tested animals at LABOKLIN (Bad Kissingen, Germany)
Species | Timeframe | PCR | IFAT/ELISA |
Dog | 2008-2020 | 5% | 27% |
Cat | 2008-2020 | 3% | 23% |
Horse | 2008-2021 | 15% | 27% |
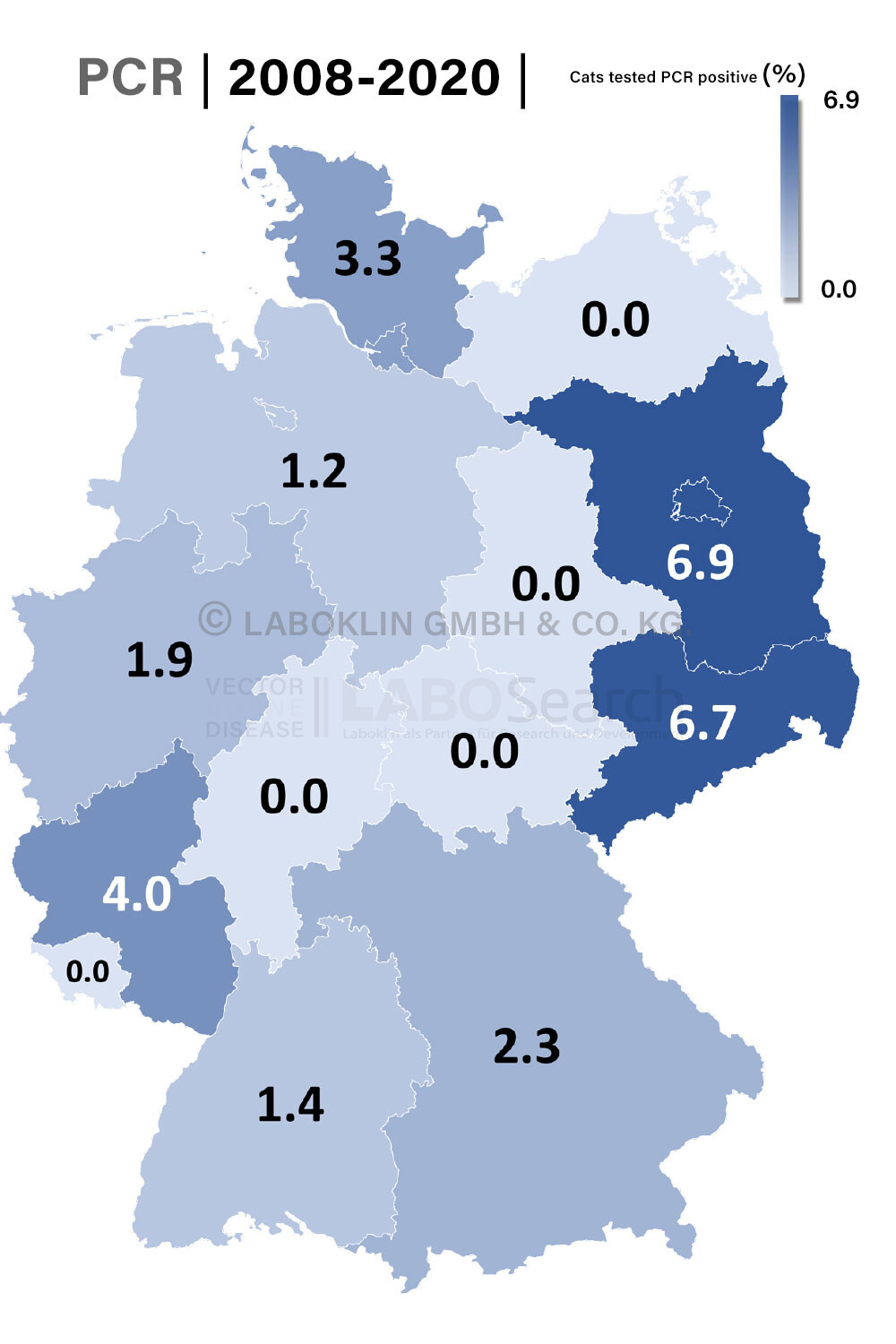
Dog (2008 – 2023, n = 137.737)
Timeframe | PCR | ELISA/IFAT |
2021-2023 | 3.8% | 32.3% |
2017-2020 | 5.2% | 34.9% |
2013-2016 | 4.6% | 18.4% |
2008-2012 | 4.3% | 26.3% |
Cat (2008 – 2023, n = 1.785)
Timeframe | PCR | ELISA/IFAT |
2021-2023 | 6.4% | 9.7% |
2017-2020 | 5.0% | 35.6% |
2013-2016 | 2.4% | 15.4% |
2008-2012 | 2.3% | 11.8% |
Horse (2008 – 2023, n = 5.876)
Timeframe | PCR | ELISA/IFAT |
2021-2023 | 13.4% | 18.1% |
2017-2020 | 16.7% | 32.7% |
2013-2016 | 17.5% | 17.6% |
2008-2012 | 3.3% | 27.5% |
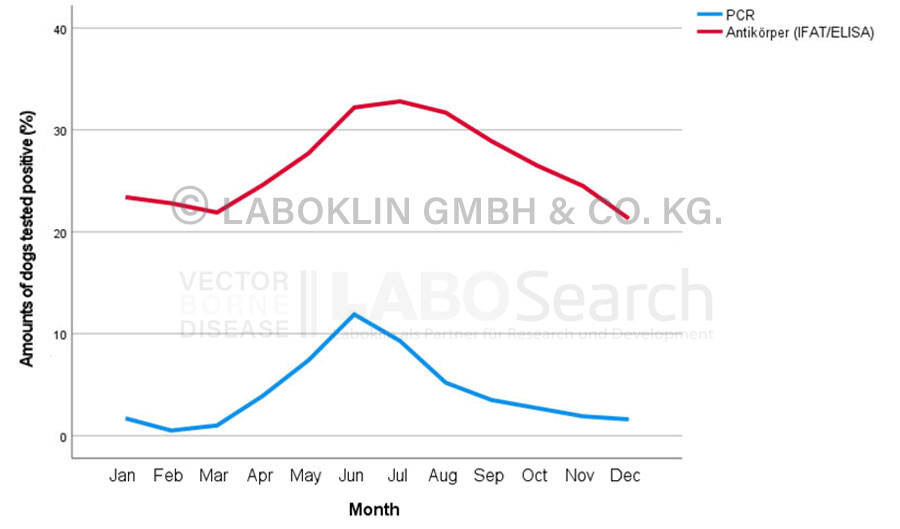
Dogs
Seasonal distribution of dogs tested positive for Anaplasma phagoytophilum by direct (PCR) and indirect test methods (IFAT, ELISA) in Germany (2008-2020, %)
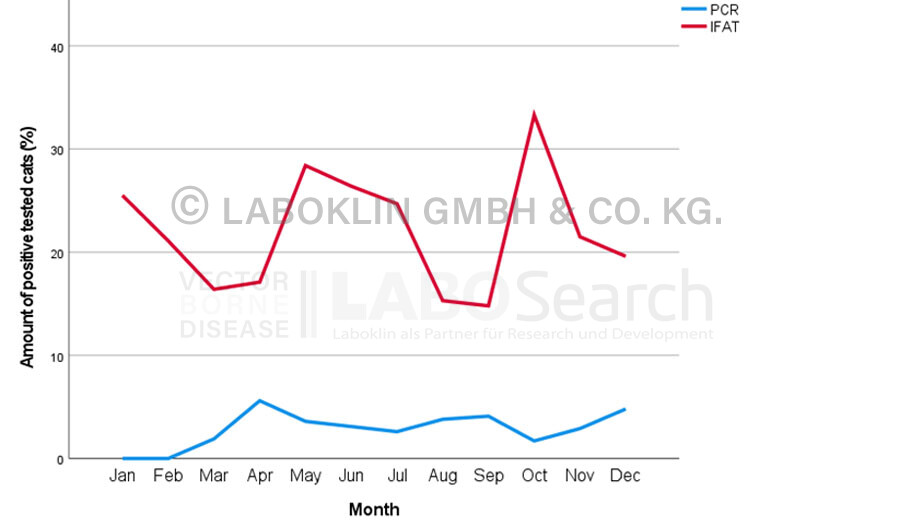
Cats
Seasonal distribution of cats tested positive for Anaplasma phagoytophilum by direct (PCR) and indirect test methods (IFAT, ELISA) in Germany (2008-2020, %)
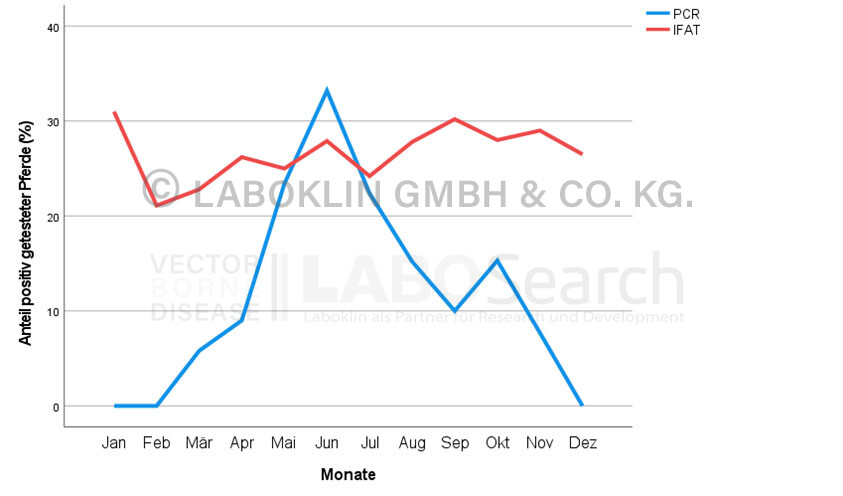
Horses
Seasonal distribution of horses tested positive for Anaplasma phagocytophilum by direct (PCR) and indirect test methods (IFAT) (2008-2021, %)