- Dirofilariosis in dogs, foxed and cats
- Zoonotic potential (humans as accidental hosts)
- Emerging disease in human medicine
- Many different species, most important:
- Dirofilaria immitis (heartworm)
- Dirofilaria repens
- Vector: mosquitoes
- Prolonged incubation periods (up to 12 years)
- Juvenile worms: microfilariae
- Adult worms: microfilariae
- Direct detection methods
- Microfilariae PCR (positive result indicative for acute infection, species differentiation after sequencing)
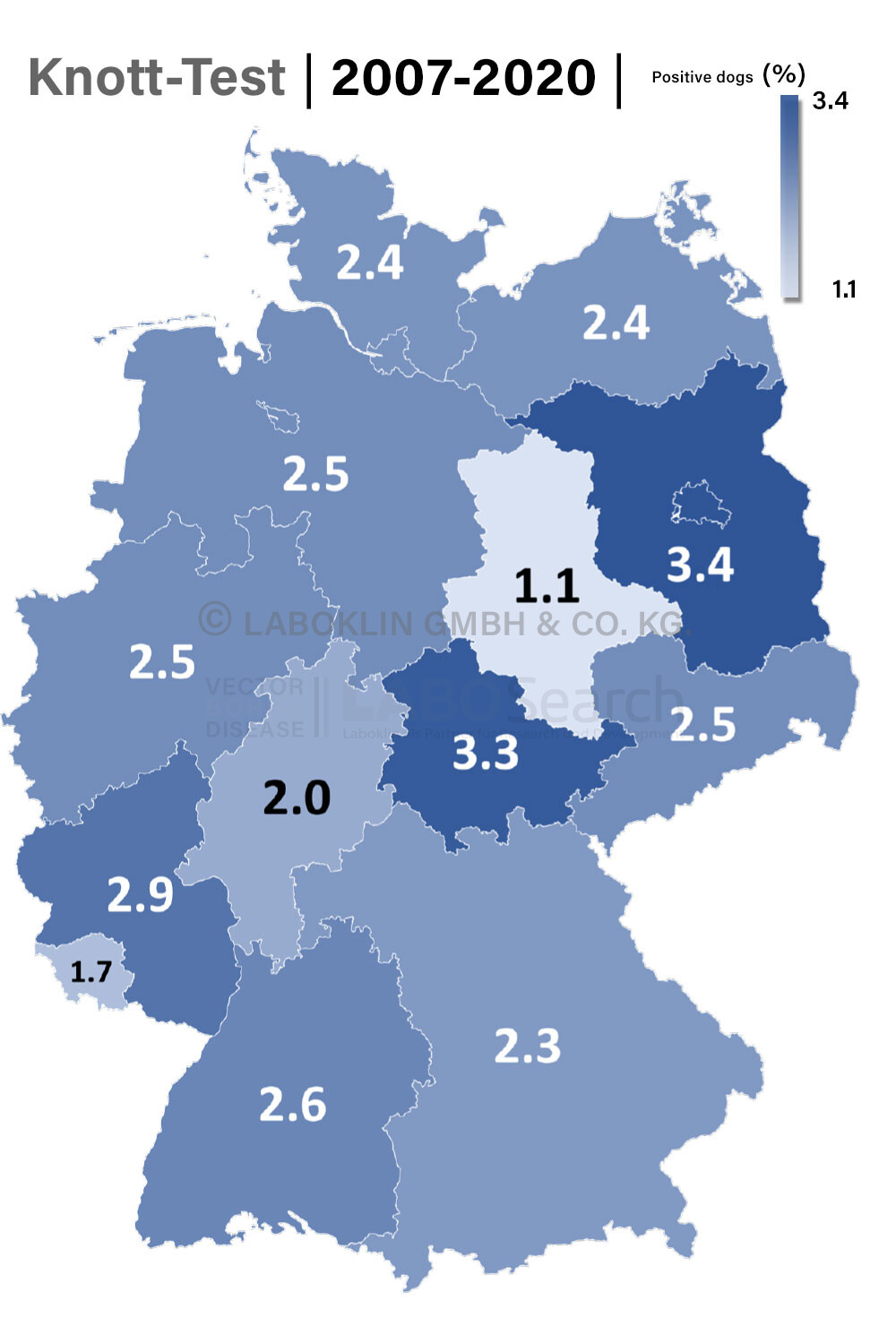
- Knott’s test (detection of microfilariae)
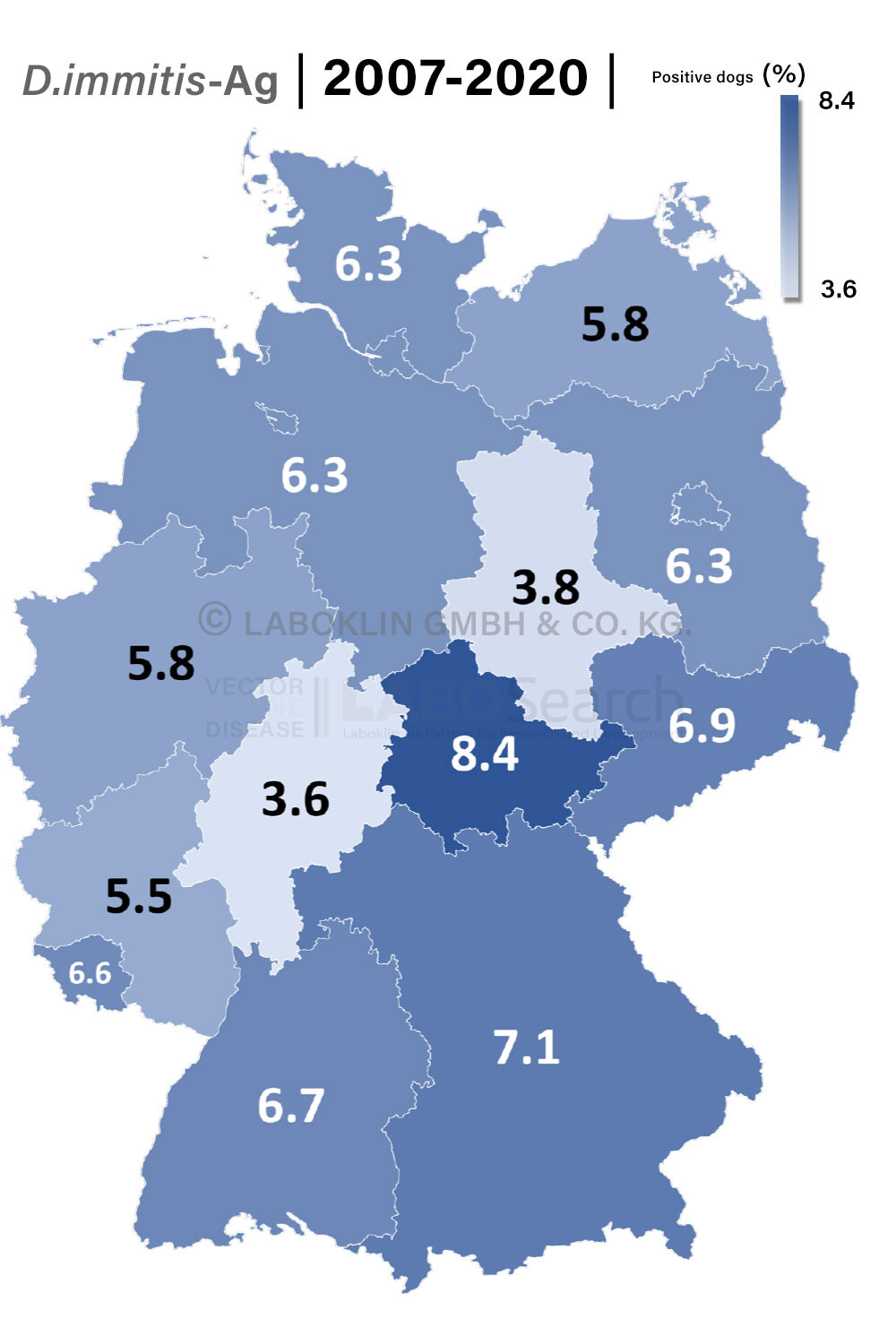
- Dirofilaria immitis antigen test (detection of female microfilariae of Dirofilaria immitis)
- Blood smear (detection of microfilariae, low sensitivity)
- Echocardiography for detection of Dirofilaria immitis
- Indirect detection methods are not established in routine diagnostics
- Dirofilaria immitis: heartworm disease with chronic coughing, dyspnea, tachypnoea, ascites (in case of low numbers of heartworms subclinical infection possible)
- Dirofilaria repens: subcutaneous noduli, not painful, pruritus possible due to subcutaneous movement of the worms, ulcerative skin lesions, most often subclinical)
- Unspecific findings in laboratory diagnostics (for example eosinophilia)
Dog (2007 – 2020)
Timeframe | Knott's test | d.immitis antigen ELISA |
N dogs | 22,085 | 21,098 |
2017-2020 | 3.8% | 6.6% |
2012-2015 | 4.0% | 5.3% |
2007-2011 | 2.3% | 3.8% |